What is the harmonics analog saturation processor?
The harmonics analog saturation processor is an electronic audio device that adds a wide spectrum of harmonics to the source signal such as an instrument or vocal recording in order to enhance the perceived tonal quality of the source signal.
The harmonic saturation processor can be used during the recording or in the post-production process for each individual track or the stereo mix.
The usual audible results are perceived as the warmer, lauder, full and rich tone when compared with the unprocessed signal. The results depend on the type and amount of harmonics or saturation added to the source signal.
How does the harmonics analog saturation processor work?
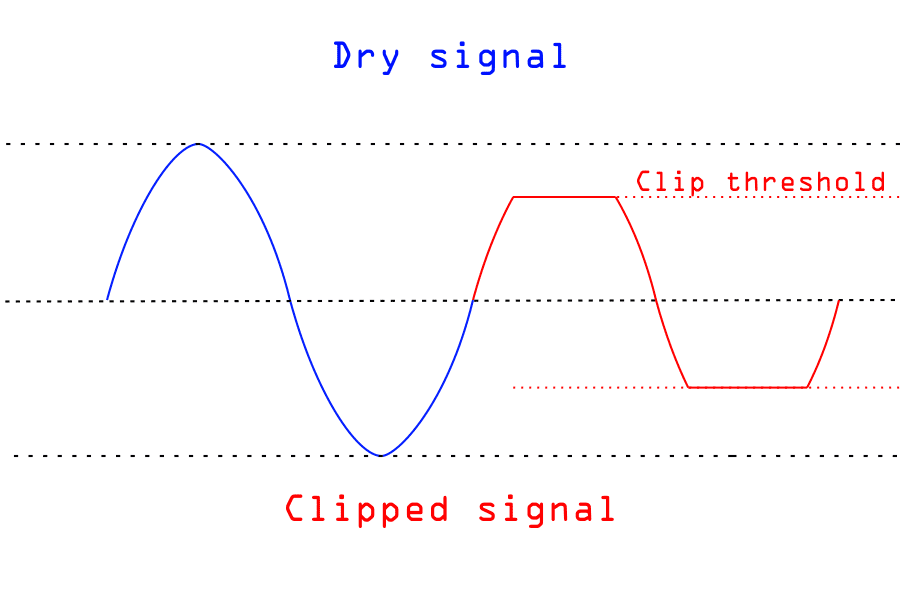
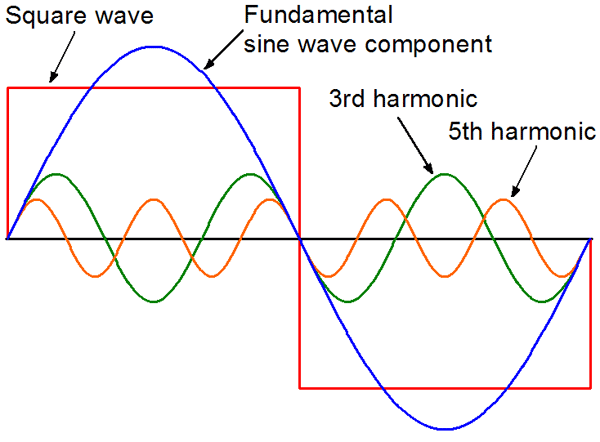
The harmonics analog saturation processor is based on the principle of generating the harmonics such as 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th, and so on, which happens when the signal is overdriven and clipped.
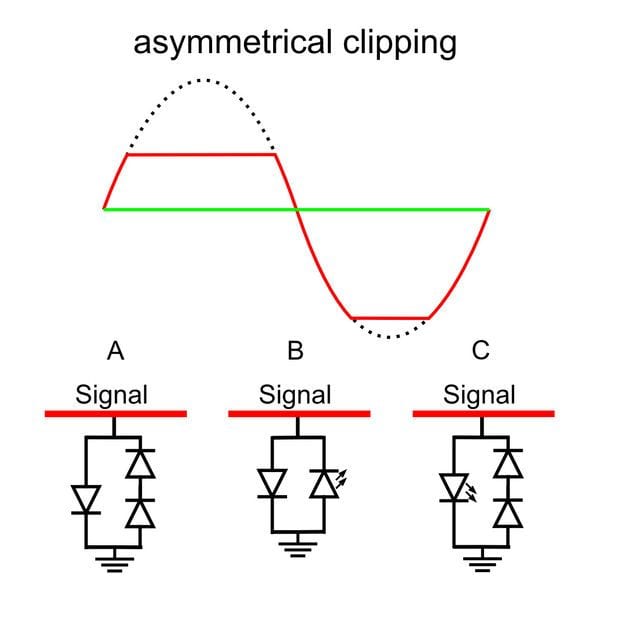
Harmonics are generated when the gain is increased or when specific electronic components are used in order to generate the harmonics, for example, the diode clipper in the guitar distortion stomp-box effect.
The simplest is to use the diode clipper or clip the signal with other active electronics components (transistors, valves). More complicated methods incorporate the VCA elements, complex circuitry based on operational amplifiers or transformers. The harmonics content can be shaped differently for specific frequencies to achieve more interesting results.
The phenomena of generating harmonics, also called THD, occurs naturally in the various audio electronic devices as a side effect of high input or high output signal or as a result of bad design. Some components such as thermionic valves or transformers produce more harmonics due to the design and physical properties. Humans perceive harmonics, especially even, as a pleasant experience.
The harmonics analog saturation processor uses the physical principles of generating the THD in electronic audio devices to produce a higher content of harmonics without the negative side effects such as increased gain and noise or high-level overdrive which might be dangerous for many audio devices.
Many different techniques are used to achieve saturation results.
The simplest is to use the diode clipper or clip the signal with other active electronics components (transistors, valves). More complicated methods incorporate the VCA elements, complex circuitry based on operational amplifiers or transformers. The harmonics content can be shaped differently for specific frequencies to achieve more interesting results.
The difference between the harmonic processor and saturation processor.
Although quite often the harmonics are the result of the saturation of audio device, the distinction should be made between the saturation processor and the harmonic processor.
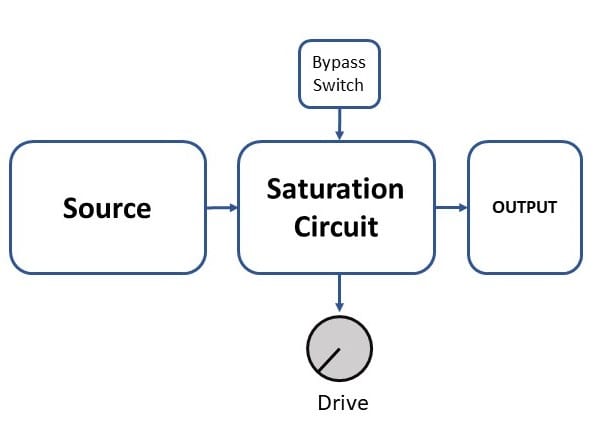
The saturation processor is usually a more simple device, where the source signal is passed through the electronic circuit and becomes saturated with harmonics generated by the processor circuitry.
The Colour Format is an example of the saturation devices. Learn More ->
The harmonic processor is a more complicated device that usually consists of a separate circuit for generating the harmonics which later can be added to the source signal.
The source signal does not pass the saturation circuitry and the amount of harmonics can be controlled independently from the source signal.
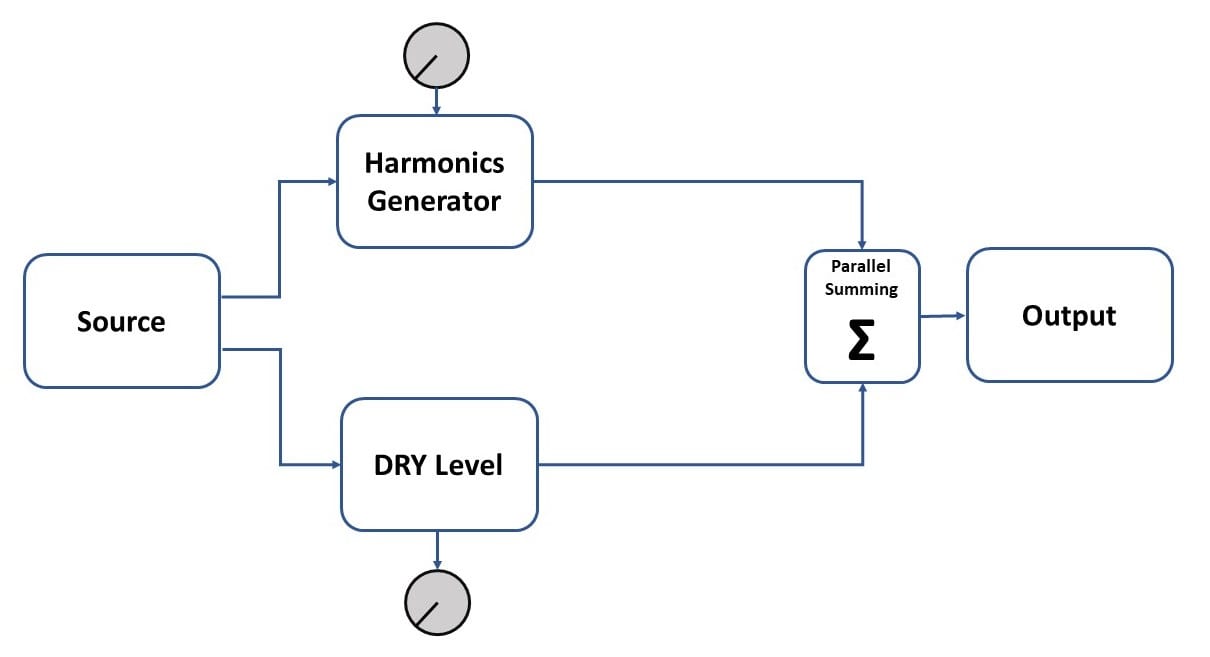 The example of the Harmonic Processors ->
The example of the Harmonic Processors ->
Links:
ST596 | Analog Harmonics Processor
ST596 | Analog Harmonics Processor – Matched Pair
Wiki
© 2025 HRK Shop
User Information. This page uses cookies files to process the orders and deliver a better user experience.